Ectopic Pregnancy
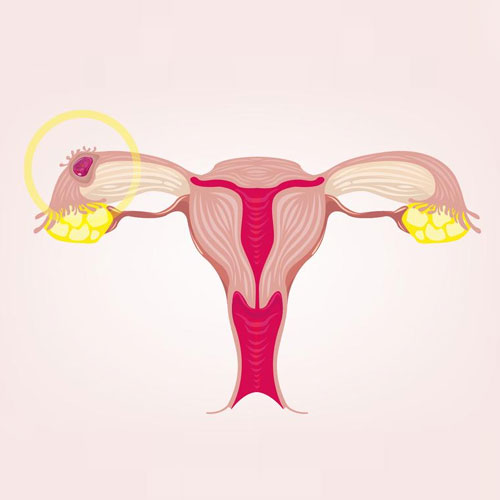
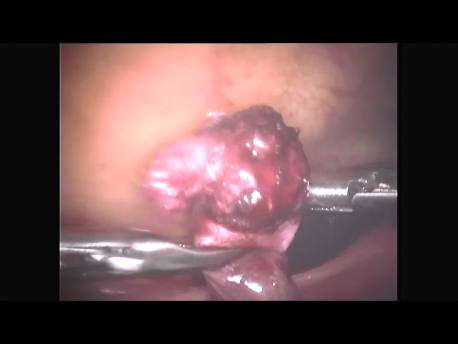
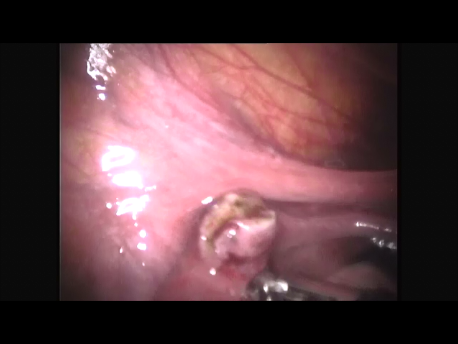
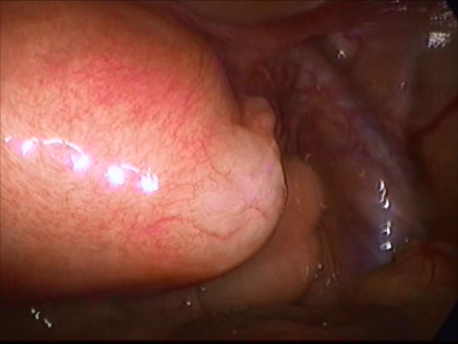
Ectopic pregnancy means a pregnancy lying outside its normal location in the uterus. The uterus is an organ ideally designed to accommodate a pregnancy since it can provide a blood supply to the growing pregnancy and expand & grow to accommodate the growing baby within. If the pregnancy implants in any other organ, it rapidly erodes into the blood vessels supplying that organ to extract oxygen and nutrition. These blood vessels rupture and bleeding occurs. If not treated rapidly, this can prove fatal for the woman.
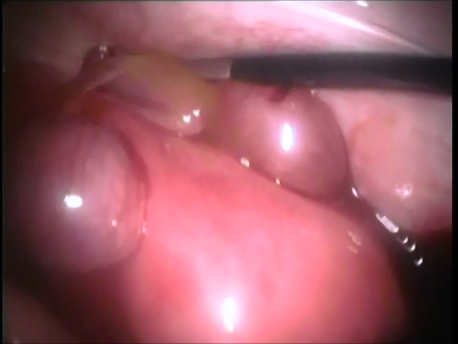
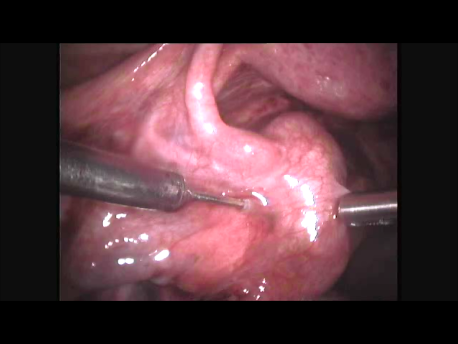
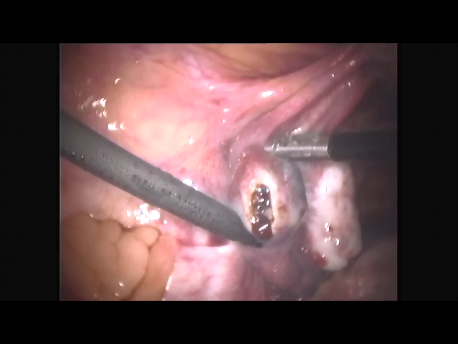
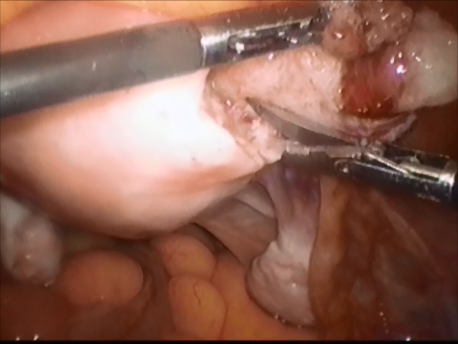
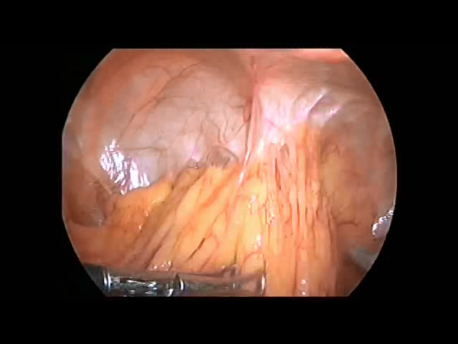
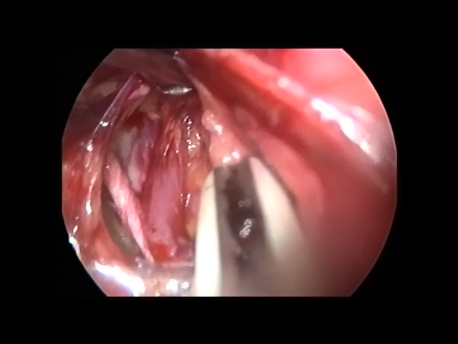
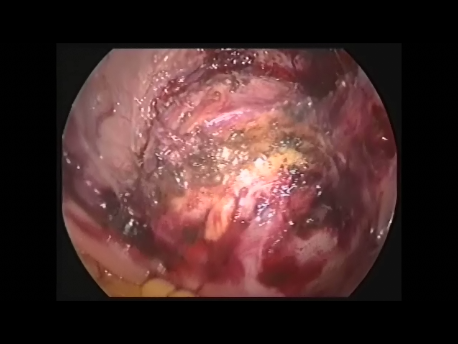
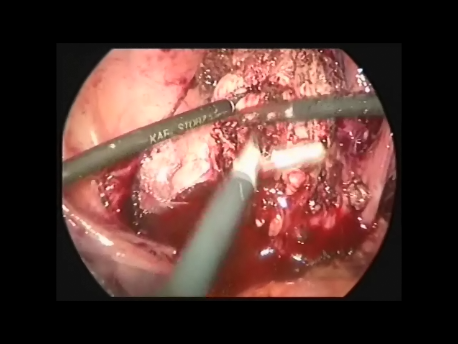
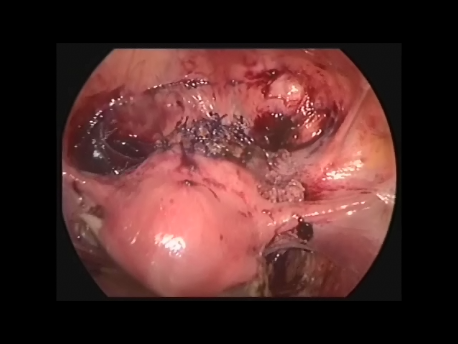
The Fallopian tube is the commonest site of an ectopic pregnancy. Other sites include the ovary, cervix, a scar of a previous cesarean section and, very rarely, other abdominal organs (intestines, spleen, etc.)
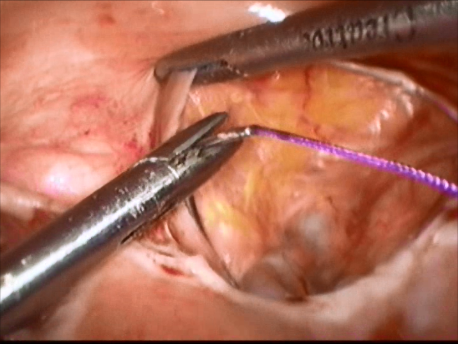
Laparoscopic surgery is the gold standard for management of ectopic pregnancy. Even with the most extreme blood loss, laparoscopic surgery is superior to conventional open surgery since it involves small incision with virtually no bleeding, rapid removal of the ectopic or the affected organ, better maintanence of blood supply to the brain of the woman (since the increased pressure in the abdomen diverts blood away from the abdominal organs to other areas) and, naturally, faster and painless recovery.