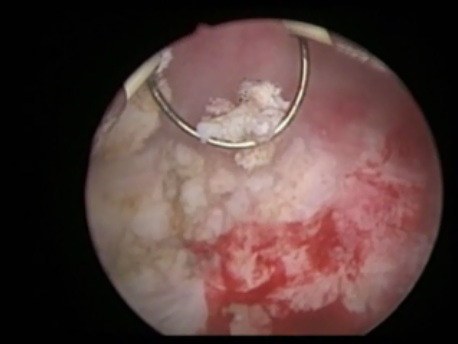
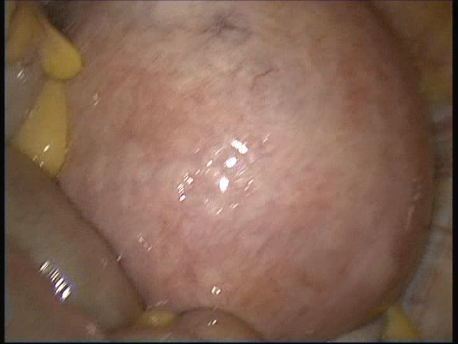
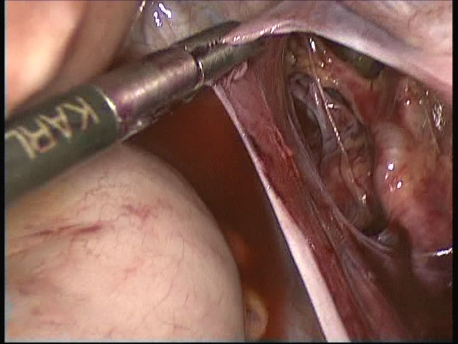
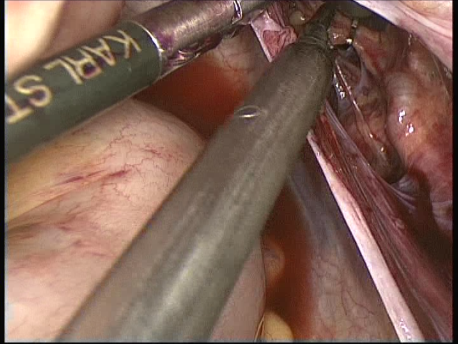
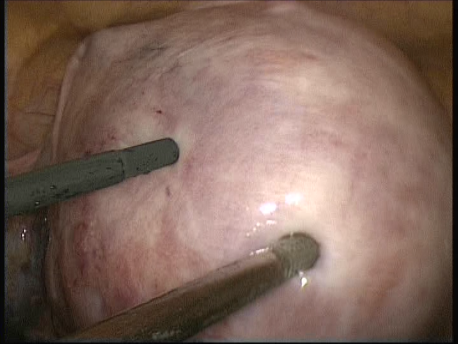
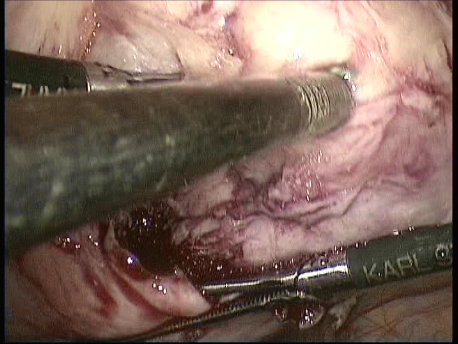
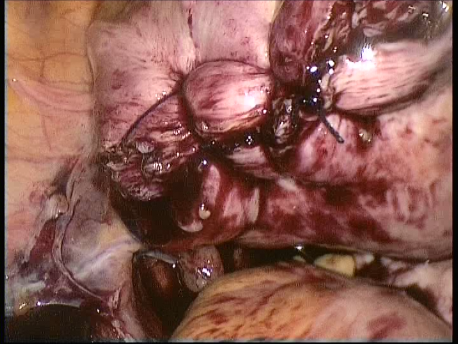
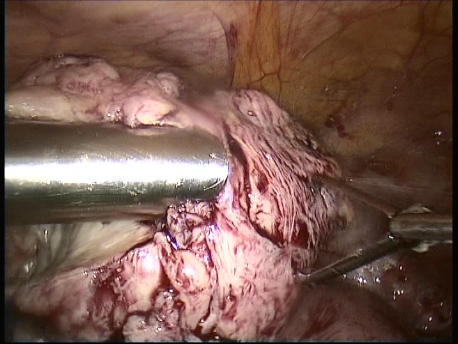
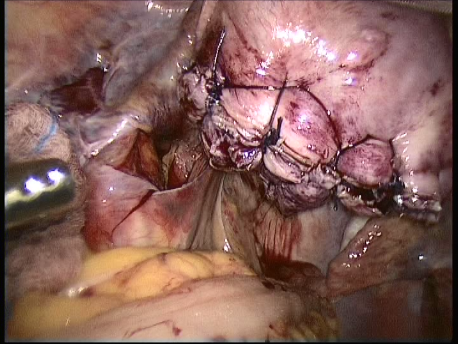
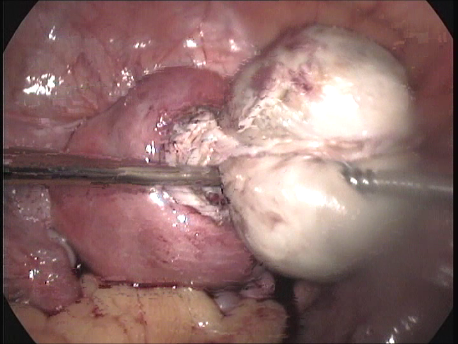
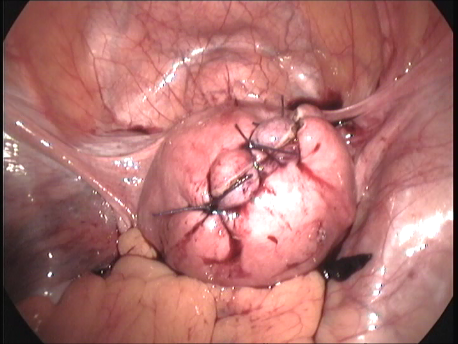
The common symptoms of leiomyomas include :
- Pain : Large tumors stretch the uterine muscle and cause pain and dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation). These tumors, by virtue of their size and compression of adjacent structures such as intestines and urinary bladder, may cause pain.
- Menstrual disturbances : Fibroids usually cause heavy and regular menses. However, a fibroid encroaching upon the cavity of the uterus may cause heavy as well as painful and irregular menstruation.
- Infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss : Large fibroids inside the uterine muscle (intramural fibroids), fibroids entering the cavity of the uterus (submucous fibroids) and fibroids compressing the Fallopian tubes can cause infertility (inability to conceive) and recurrent miscarriage.
- Other symptoms : Extremely large fibroids may press upon the rectum and cause difficulty in passing stools. They may press upon the urinary bladder and may cause increased feeling of passing urine or difficulty in passage of urine. They may compress the ureter (tubes taking urine from the kidneys to the bladder) and cause their dilatation. Part of the fibroid may die out due to reduced blood supply (necrosis and degeneration) and cause fever and intense pain. A fibroid lying on the outer surface of the uterus (subserosal fibroids) may have a thin attachment(pedicle) to the uterus (pedunculated fibroids) and undergo twisting (torsion) of the pedicle. This causes severe pain and requires emergency laparoscopic surgery.