Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy means removal of the uterus. Laparoscopic hysterectomy is removal of the uterus by laparoscopy. This procedure involves placement of 3-4 small tubes (cannulae) 0.5-1cm in diameter in the abdomen and passing a telescope along with specialized instruments through these cannulae for performing this surgery.
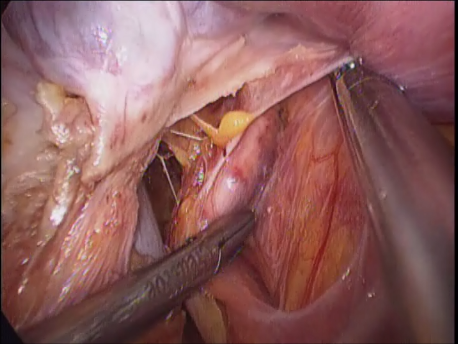
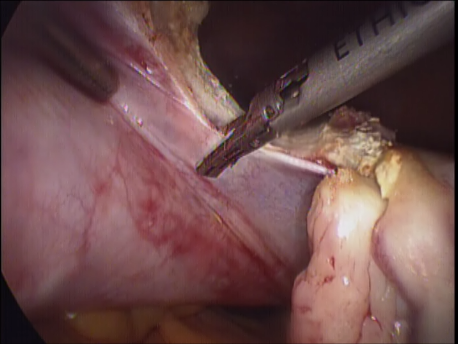
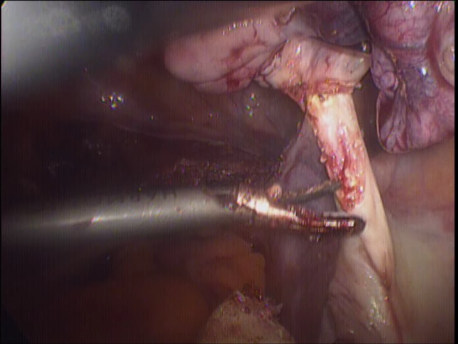
The uterus is fixed in the pelvis by cord or band like structures called ligaments. In the lower part it is closely adherent to the urinary bladder in front and the rectum behind. The uterus is attached to the top of the vagina and derives its blood supply from two large vessels (uterine arteries) running on either side of the uterus.
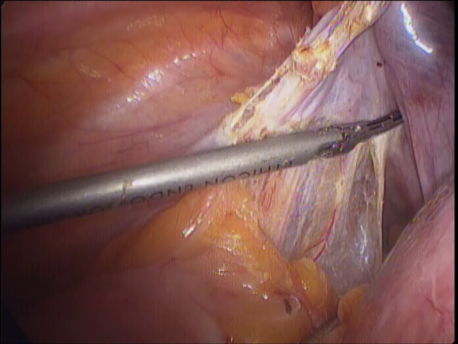
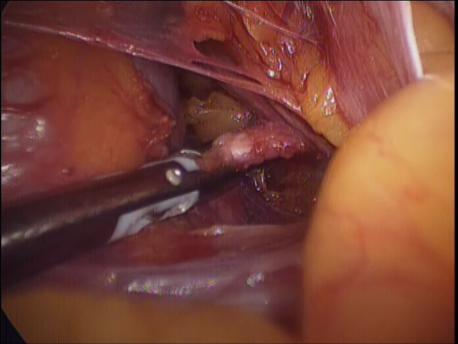
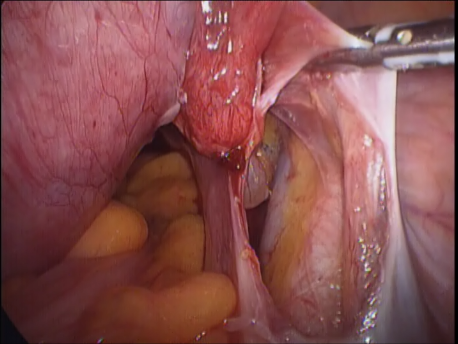
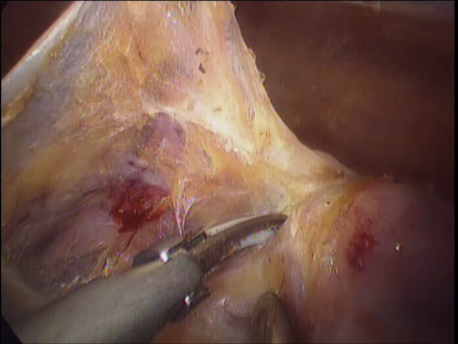
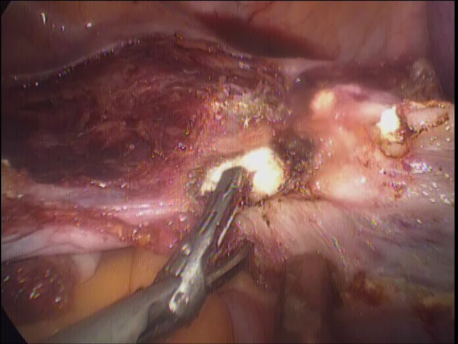
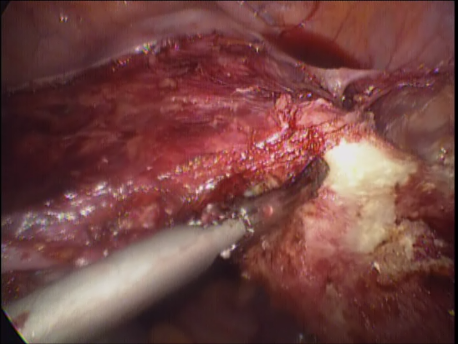
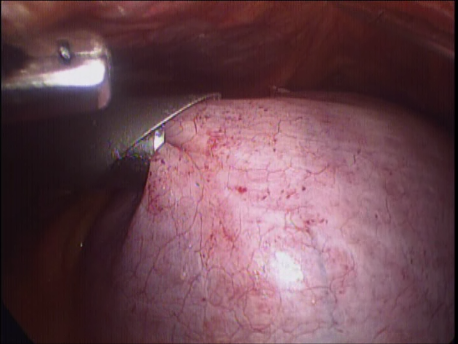
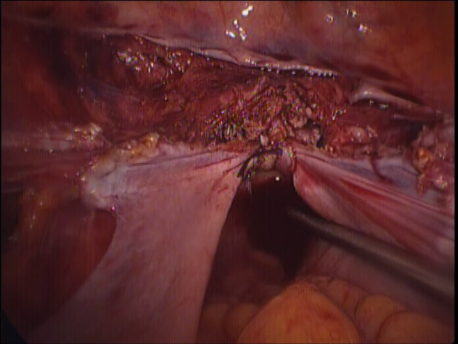
Laparoscopic hysterectomy involves separation of the uterus from its attachments (ligaments, Fallopian tubes and ovaries), dissection of the urinary bladder and rectum safely away from the uterus, cauterizing or suturing & cutting the blood supply (uterine arteries) and cutting the uterus from the top of the vagina. The uterus is removed through the vagina or through a machine called a morcellator which cuts the uterus into long strips. The vagina is sutured with absorbable sutures.
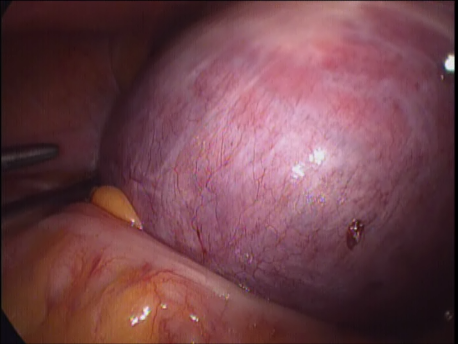
The Fallopian tubes are usually removed to prevent a hydrosalpinx (fluid filled swelling of the Fallopian tubes) later. The ovaries are removed (one or both) if they are diseased or have stopped functioning (menopause).